Physical inspection protocols are the backbone of quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and operational excellence across countless industries worldwide.
Whether you’re managing manufacturing facilities, overseeing construction sites, conducting safety audits, or ensuring food service standards, having robust inspection protocols isn’t just good practice—it’s essential for business continuity, legal protection, and customer satisfaction. Yet many organizations struggle with inconsistent procedures, incomplete documentation, and compliance gaps that expose them to significant risks.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about creating, implementing, and maintaining physical inspection protocols that deliver results while keeping your operations compliant and efficient.
🔍 Understanding the Foundation of Physical Inspection Protocols
Physical inspection protocols represent systematic approaches to examining equipment, facilities, products, or environments against predetermined standards. These protocols serve multiple critical functions within an organization, from preventing equipment failures to satisfying regulatory requirements.
The most effective inspection protocols share several common characteristics. They’re documented clearly, repeatable across different inspectors, measurable in their outcomes, and aligned with both industry standards and organizational objectives. Without these foundational elements, inspections become subjective exercises that fail to deliver consistent value.
Organizations that excel at physical inspections understand that protocols must evolve alongside changing regulations, technological advances, and operational needs. Static checklists from five years ago rarely address today’s compliance landscape or leverage modern inspection tools that can dramatically improve efficiency.
The Business Case for Structured Inspection Protocols
Companies investing in comprehensive inspection protocols consistently report measurable returns. Reduced equipment downtime, fewer compliance violations, lower insurance premiums, and decreased liability exposure all contribute to substantial cost savings that typically exceed implementation investments within the first year.
Beyond financial benefits, structured protocols enhance organizational reputation. Customers, partners, and regulators view documented inspection processes as indicators of operational maturity and commitment to quality. This perception opens doors to contracts and partnerships that prioritize vendors with proven compliance records.
📋 Core Components of Effective Inspection Protocols
Every robust inspection protocol includes several essential elements that work together to ensure thoroughness and consistency. Understanding these components helps you build protocols that actually get used rather than gathering dust in compliance binders.
Clear Inspection Objectives and Scope
Before developing specific procedures, define precisely what you’re inspecting and why. Vague objectives lead to incomplete inspections and documentation gaps. Your protocol should explicitly state what areas, equipment, or processes fall within scope, what you’re evaluating them against, and what outcomes you expect from the inspection process.
Scope definition prevents mission creep during inspections while ensuring nothing critical gets overlooked. When inspectors understand boundaries, they can focus attention appropriately rather than wasting time on tangential observations or missing key checkpoints.
Detailed Step-by-Step Procedures
Effective protocols break down inspections into logical sequences that inspectors can follow systematically. Each step should include specific actions, expected observations, measurement requirements, and documentation needs. Ambiguous instructions like “check equipment condition” should be replaced with precise criteria such as “verify no visible corrosion exceeding 2mm depth on joint surfaces.”
Sequential procedures also incorporate safety protocols, required tools or equipment, and estimated time allocations. This completeness ensures inspectors arrive prepared and can complete inspections efficiently without repeated site visits for forgotten measurements or documentation.
Standardized Documentation Requirements
Documentation transforms observations into actionable intelligence and compliance evidence. Your protocols must specify exactly what information inspectors record, in what format, and with what level of detail. Standardization enables meaningful comparison across time periods, locations, and inspectors.
Modern inspection protocols increasingly incorporate photographic or video evidence requirements, particularly for conditions that might deteriorate before remediation or for compliance verification. Clear documentation standards prevent the common problem of insufficient evidence when disputes or audits occur months after inspections.
🛠️ Designing Inspection Checklists That Actually Work
Checklists represent the practical manifestation of your inspection protocols. Poorly designed checklists confuse inspectors, slow processes, and produce unreliable data. Exceptional checklists guide inspectors efficiently through complex evaluations while capturing all necessary information.
Balancing Comprehensiveness with Usability
The tension between thorough coverage and practical usability challenges every inspection program. Excessively detailed checklists overwhelm inspectors and increase completion time to impractical levels. Conversely, overly simplified checklists miss critical observations and provide false confidence in inspection completeness.
The solution lies in risk-based prioritization. Focus detailed attention on high-risk areas while streamlining coverage of lower-risk elements. Variable-depth checklists that adjust based on initial findings provide thorough investigation when issues arise without burdening routine inspections with unnecessary detail.
Incorporating Conditional Logic
Advanced inspection protocols use conditional pathways that respond to inspector findings. If an inspector identifies a particular condition, the protocol automatically directs them to additional related checkpoints. This intelligent branching ensures thorough investigation of problems without cluttering base checklists with rarely-needed items.
Digital inspection tools excel at implementing conditional logic that would be cumbersome with paper checklists. These systems guide inspectors through complex decision trees seamlessly, ensuring consistency while adapting to actual conditions encountered.
📱 Leveraging Technology for Inspection Excellence
Digital transformation has revolutionized physical inspection capabilities. Organizations clinging to clipboard-and-paper approaches miss substantial efficiency gains and enhanced data quality that modern tools provide.
Mobile Inspection Applications
Smartphone and tablet apps designed for inspections eliminate transcription errors, enable real-time data capture, and facilitate immediate reporting. Inspectors photograph issues directly within inspection records, timestamp observations automatically, and upload completed inspections from field locations without returning to offices.
These applications often include offline functionality essential for inspections in areas without reliable connectivity. Data syncs automatically when connections restore, preventing lost information while enabling inspections anywhere.
Quality inspection management requires purpose-built tools that understand compliance requirements and inspection workflows. Several platforms specifically address physical inspection needs across various industries.
Integration with Asset Management Systems
Standalone inspection data provides limited value compared to information integrated with broader asset management and maintenance systems. Modern protocols ensure inspection findings automatically trigger work orders, update asset condition records, and inform predictive maintenance algorithms.
This integration creates closed-loop processes where inspections drive actions rather than simply documenting conditions. Organizations achieve this through API connections between inspection tools and enterprise asset management platforms, ensuring seamless data flow without manual transfers.
👥 Training Inspectors for Consistent Results
Even perfectly designed protocols fail without properly trained inspectors who understand both procedures and underlying principles. Training investments directly correlate with inspection quality and organizational compliance outcomes.
Developing Comprehensive Training Programs
Effective inspector training extends beyond simply reviewing checklists. Comprehensive programs cover relevant regulations and standards, explain the reasoning behind specific inspection criteria, demonstrate proper measurement techniques, and provide extensive practice with feedback before independent inspections.
Training should address common challenges inspectors encounter, including ambiguous conditions, access difficulties, and situations requiring judgment calls. Role-playing exercises and scenario discussions build confidence in handling unexpected circumstances consistently.
Certification and Competency Verification
Many industries require inspector certification through recognized bodies. Even where not mandated, formal competency verification ensures inspectors meet minimum capability standards. Your protocols should specify required qualifications, recertification intervals, and processes for verifying ongoing competency.
Periodic quality audits where experienced inspectors accompany and evaluate others identify training gaps and ensure consistency across your inspection team. These audits also provide opportunities for continuous protocol refinement based on field experience.
📊 Analyzing Inspection Data for Continuous Improvement
Inspection data represents valuable organizational intelligence that extends far beyond individual compliance verification. Systematic analysis reveals trends, predicts failures, and identifies improvement opportunities that reactive approaches miss entirely.
Trend Identification and Predictive Insights
Aggregating inspection findings over time highlights patterns invisible in individual reports. Gradually deteriorating conditions become evident, enabling proactive interventions before failures occur. Geographic or operational patterns might reveal systemic issues requiring fundamental process changes rather than repetitive repairs.
Advanced analytics apply machine learning to inspection histories, identifying subtle correlations between conditions and eventual failures. These predictive models enable truly preventive maintenance that addresses problems before they manifest, maximizing asset life while minimizing disruption.
Key Performance Indicators for Inspection Programs
Measuring inspection program effectiveness requires appropriate metrics beyond simple completion rates. Consider tracking indicators such as:
- Percentage of inspections completed within scheduled windows
- Average time from issue identification to resolution
- Repeat finding rates indicating unresolved underlying problems
- Inspector consistency scores comparing findings across team members
- Compliance violation rates during external audits
- Cost savings attributed to proactive issue identification
Regular review of these metrics with leadership demonstrates inspection program value while identifying areas requiring additional resources or process adjustments.
⚖️ Navigating Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Inspection protocols must satisfy applicable regulatory frameworks while remaining practical for field implementation. Understanding compliance landscapes prevents both inadequate protocols that expose organizations to violations and excessive procedures that waste resources.
Industry-Specific Compliance Considerations
Regulatory requirements vary dramatically across industries. Manufacturing facilities face OSHA safety inspection mandates alongside industry-specific quality standards. Food service operations must satisfy health department protocols. Construction sites navigate building code compliance and safety regulations simultaneously.
Your protocols should explicitly reference applicable regulations, incorporating specific requirements directly into inspection procedures. This integration ensures compliance verification occurs naturally during routine inspections rather than requiring separate audit preparations.
Documentation for Regulatory Defense
When regulators question compliance, your inspection records provide primary defense evidence. Protocols must ensure documentation sufficiently demonstrates due diligence and reasonable precautions. This requires not just recording compliant conditions but also documenting corrective actions taken when issues arise.
Retention requirements for inspection records vary by jurisdiction and industry. Your protocol should specify retention periods and storage methods that satisfy all applicable requirements while remaining practically manageable as records accumulate over years.
🔄 Implementing and Maintaining Your Inspection Protocols
Even brilliantly designed protocols fail without proper implementation and ongoing maintenance. Successful adoption requires change management, stakeholder buy-in, and systems for continuous protocol evolution.
Phased Rollout Strategies
Organization-wide protocol changes implemented simultaneously often overwhelm teams and encounter resistance. Phased approaches that pilot new protocols in limited areas allow refinement based on real-world feedback before broader deployment.
Pilot programs identify practical challenges, technology issues, and training gaps in controlled environments where adjustments cause minimal disruption. Early adopters become champions who facilitate later rollout phases through peer influence and practical advice.
Creating Feedback Loops for Protocol Refinement
Inspection protocols require regular updates reflecting regulatory changes, technology advances, and lessons learned from implementation experience. Establish formal mechanisms for inspectors to suggest improvements based on field challenges they encounter.
Quarterly or semi-annual protocol reviews with cross-functional teams ensure procedures remain current and practical. These reviews consider regulatory updates, incident investigations that revealed inspection gaps, and technological opportunities for enhanced efficiency.
💡 Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Organizations implementing new inspection protocols typically encounter predictable obstacles. Anticipating these challenges enables proactive mitigation strategies that smooth adoption.
Resistance to Change and Process Adoption
Inspectors comfortable with existing approaches often resist new protocols, particularly when technology replaces familiar paper processes. Address resistance through early involvement in protocol development, clear communication about benefits, and recognition for early adopters who embrace changes.
Demonstrating how new protocols make inspectors’ work easier rather than simply adding requirements improves acceptance. Focus messaging on efficiency gains, reduced paperwork, and enhanced professional development opportunities rather than compliance mandates.
Resource Constraints and Competing Priorities
Inspection programs compete for limited organizational resources against other priorities. Building leadership support requires demonstrating clear returns on inspection investments through risk reduction, compliance cost avoidance, and operational efficiency improvements.
Quantify potential costs of inspection program failures, including regulatory fines, liability exposure, and operational disruptions. Compare these risks against relatively modest implementation costs to build compelling business cases for adequate resource allocation.
🚀 Future-Proofing Your Inspection Protocols
Inspection methodologies continue evolving as technology advances and regulatory frameworks develop. Forward-thinking organizations build adaptability into protocols, positioning themselves to leverage emerging capabilities as they mature.
Emerging Technologies Transforming Inspections
Drone-based inspections enable safe, efficient examination of difficult-to-access areas like roofs, towers, and industrial equipment. Internet-of-Things sensors provide continuous condition monitoring that supplements periodic physical inspections with real-time data streams.
Artificial intelligence increasingly analyzes inspection photographs automatically, identifying conditions human inspectors might miss while dramatically reducing analysis time. Augmented reality overlays guide inspectors through complex procedures while highlighting relevant information in their field of view.
Building protocols with modular structures facilitates technology integration as these capabilities become practical for your operations. Rather than wholesale protocol rewrites, modular approaches enable targeted updates incorporating new tools while maintaining proven process elements.
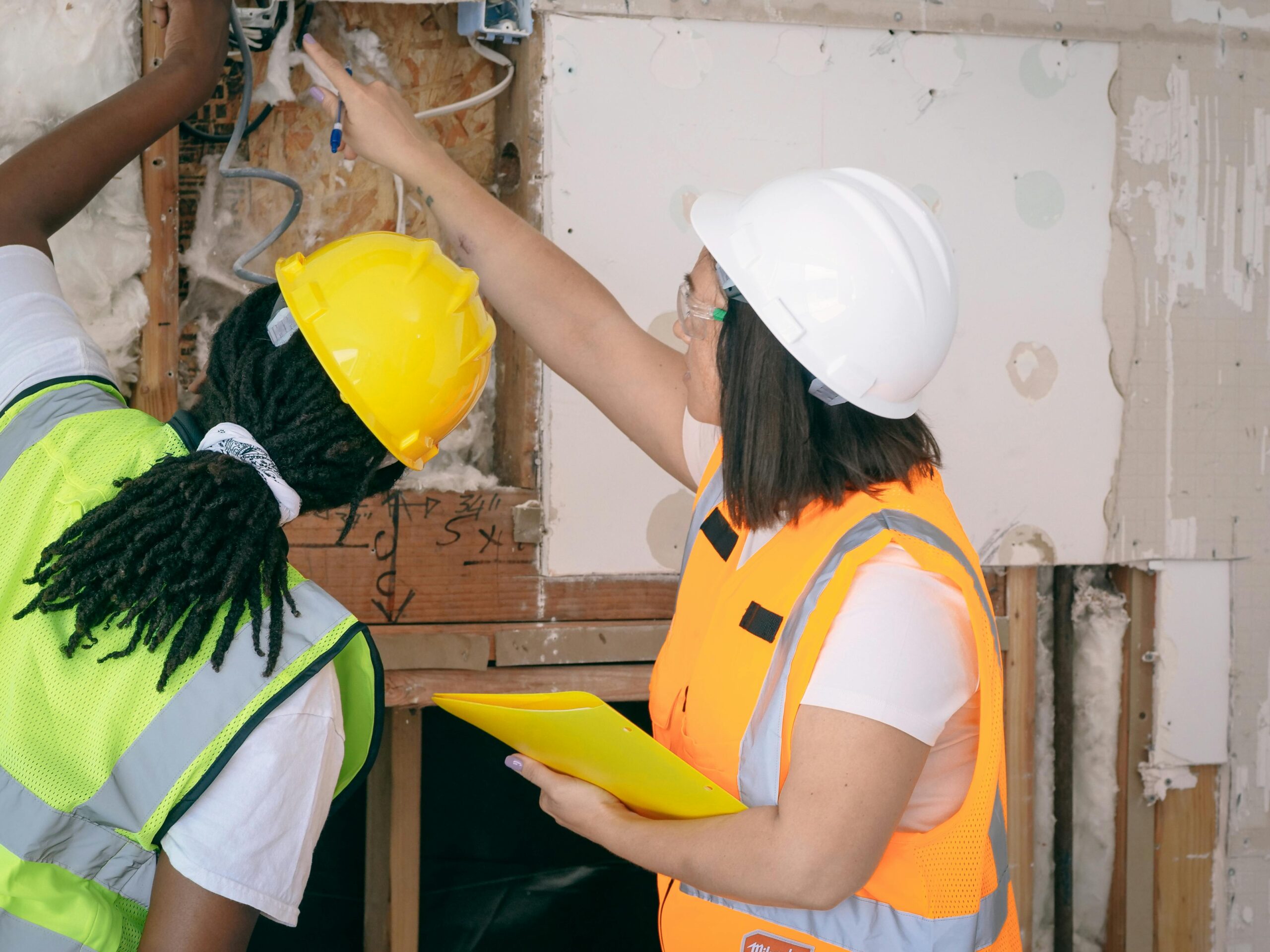

🎯 Measuring Success and Demonstrating Value
Sustaining organizational commitment to inspection excellence requires ongoing demonstration of program value. Comprehensive measurement frameworks translate inspection activities into business outcomes leadership understands and values.
Develop dashboards presenting inspection metrics alongside operational and financial indicators they influence. Connect inspection completion rates with equipment uptime, compliance scores with avoided regulatory costs, and issue identification rates with prevented failures. These connections make abstract inspection activities concrete through tangible business impacts.
Regular reporting to leadership maintains visibility and reinforces inspection programs as strategic investments rather than overhead costs. Celebrate successes when inspections prevent significant incidents, identify cost-saving opportunities, or enable smooth regulatory audits without findings.
Physical inspection protocols represent far more than bureaucratic compliance exercises. When properly designed, implemented, and maintained, they become strategic assets that protect organizations from risks, optimize operations, and demonstrate commitment to excellence. The investment in developing robust inspection protocols pays dividends through reduced incidents, lower compliance costs, extended asset life, and enhanced organizational reputation.
Organizations that master physical inspection protocols position themselves for sustainable success in increasingly regulated, competitive environments. Whether you’re just beginning to formalize inspection processes or refining mature programs, the principles outlined in this guide provide a roadmap toward inspection excellence that delivers measurable business value while ensuring flawless compliance. Start with clear objectives, build comprehensive yet practical protocols, train your team thoroughly, leverage appropriate technology, and commit to continuous improvement—and you’ll transform inspections from dreaded obligations into strategic advantages.
Toni Santos is a production systems researcher and industrial quality analyst specializing in the study of empirical control methods, production scaling limits, quality variance management, and trade value implications. Through a data-driven and process-focused lens, Toni investigates how manufacturing operations encode efficiency, consistency, and economic value into production systems — across industries, supply chains, and global markets. His work is grounded in a fascination with production systems not only as operational frameworks, but as carriers of measurable performance. From empirical control methods to scaling constraints and variance tracking protocols, Toni uncovers the analytical and systematic tools through which industries maintain their relationship with output optimization and reliability. With a background in process analytics and production systems evaluation, Toni blends quantitative analysis with operational research to reveal how manufacturers balance capacity, maintain standards, and optimize economic outcomes. As the creative mind behind Nuvtrox, Toni curates production frameworks, scaling assessments, and quality interpretations that examine the critical relationships between throughput capacity, variance control, and commercial viability. His work is a tribute to: The measurement precision of Empirical Control Methods and Testing The capacity constraints of Production Scaling Limits and Thresholds The consistency challenges of Quality Variance and Deviation The commercial implications of Trade Value and Market Position Analysis Whether you're a production engineer, quality systems analyst, or strategic operations planner, Toni invites you to explore the measurable foundations of manufacturing excellence — one metric, one constraint, one optimization at a time.